DUNMAN HIGH school
FOUR I!<3
a bunch of people highly interested in the functions of our HOLY NOSE.=)
INTRODUCTION
Main structure
The Nose, is an organ of smell, and also part of the apparatus of respiration and voice. It can be divided into an external portion - the visible projection portion, to which the term nose is popularly restricted and an internal portion- consisting of two principal cavities (nasal fossae) separated from each other by a vertical septum, and subdivided by spongy or turbinated bones that project from the outer wall into three passages (meatuses), with which various sinuses in the ethmoid, sphenoid, frontal, and superior maxillary bones communicate by narrow openings.
The margins of the nostrils are usually lined with a number of stiff hairs (vibrissae) that project across the openings and serve as a filter in the passage of foreign substances, such as dust and small insects, which might otherwise be drawn up with the current of air intended for respiration.
The skeleton, or framework, of the nose is partly composed of the bones forming the top and sides of the bridge, and partly of cartilages. On either side are an upper lateral and a lower lateral cartilage, to the latter of which are attached three or four small cartilaginous plates, termed sesamoid cartilages. The cartilage of the septum separates the nostrils and, in association posteriorly with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and with the vomer, forms a complete partition between the right and left nasal fossae.
The nasal fossae, which constitute the internal part of the nose, are lofty and of considerable depth. They open in front through the nostrils and behind end in a vertical slit on either side of the upper pharynx, above the soft palate, and near the orifices of the Eustachian tubes, leading to the tympanic cavity of the ear.
In the olfactory region of the nose the mucous membrane is very thick and colored by a brown pigment. The olfactory nerve, or nerve of smell, terminates in the nasal cavity in several small branches; these ramify in the soft mucous membrane and end in tiny varicose fibers that in turn terminate in elongated epithelial cells projecting into the free surface of the nose
FUNCTIONS
1. Warmed
2. Filtered from large particles
3. Moistened
These three functions are performed as the air passes over ridges named the
Superior, middle and inferior conchea and also as the air passes through the folds between the conchea termed the superior, middle and inferior meatus.
All these structures are highly vascularised and moistened by copious amount of mucus. This rich blood supply causes the air to be warmed to almost body temperature. As hot air can contain a higher amount of moisture, the air is also humidified to almost 100% as it passes through the nose.
Apart from heating and moistening the air, the conchea produce turbulence in the incoming air. This turbulence would induce any large particles including dust and bacteria, to stick to the mucus. Thus the air is also filtered as it is passing through the nose. This function is complimented by the presence of hairs at the entrance of the nose that trap the very large particles.
Apart from the "airconditioning" function, the nose accommodates the sense of smell, through the presence of special neuroepithelium . These sensory nerve endings are stimulated by chemicals that dissolve in the moist coating. Vocal sounds are also produced in the nasal cavity thus aiding in vocalisation.
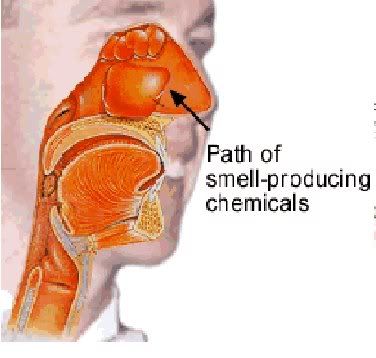
 INSIDE THE NOSE
INSIDE THE NOSE

The uppermost portion of the human respiratory system, the nose is a hollow air passage that functions in breathing and in the sense of smell.
The nasal cavity moistens and warms incoming air, while small hairs and mucous filter out harmful particles and microorganisms. This illustration depicts the interior of the human nose.
When smell-producing chemicals come into contact with the upper portion of the nasal passage, the smell is carried by nerve fibres through the roof of the nose into the brain.
 Air normally enters the nose where it is:
Air normally enters the nose where it is:
 NOW AREN'T YOU MORE EQUIPPED WITH MORE KNOWLEDGE ON THE NOSE?=)))))
NOW AREN'T YOU MORE EQUIPPED WITH MORE KNOWLEDGE ON THE NOSE?=)))))
